The Science
New Approaches
Obesity is complex because it results from wide spectrums of causatives that involve genetic and hormonal imbalances, chronic inflammation, gut microbiomes, and environmental factors. We set new strategies in search of putative neutraceuticals; we examined best-known herbs that balance essential physiological processes in human. Our adventure began with Gynostemma pentaphyllum. It is a well-known herb as an elixir of life that has been used in Korea, Japan, and China for more than 500 years. Series of molecular and cellular functional research of the materials extracted from Gynostemma pentaphyllum gave rise to Actiponin® as a nutraceutical which counteracts obesity. We demonstrated that Actiponin® actively reduces fat mass of the 3 different types of abdominal fat layers by up to 11 % in clinical studies of Korean (Obesity 22:63)

Actiponin®
Activates AMPK
Actiponin® delivers its biological function through the activation of AMPK (Bioorg Med Chem 19:6254, 2011). In particular, AMPK controls most critical cellular functions including energy homeostasis, autophagy, mitochondrial biogenesis, and cellular survival and proliferation (for review, see Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 19: 121). It is thus most probable that Actiponin® is able to modulate the diseases that are associated with AMPK.
AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) is a very sophisticated enzyme to sense low cellular ATP level, enabling cells to adapt their metabolism to meet their energy or nutrients needs. For instance, when cells are facing low energy situation, AMPK as a serine/threonine kinase phosphorylates specific enzymes to increase ATP synthesis but decrease ATP consumption. As seen in Figure 1, AMPK governs essential biological processes including energy homeostasis, protein metabolism, autophagy, mitochondrial homeostasis, mTOR signaling pathway, immune response and cellular homeostasis. AMPK is a critical mediator in controlling the cellular response to energetic stress, abnormal cellular conditions, autophagy, and immunological disorders.
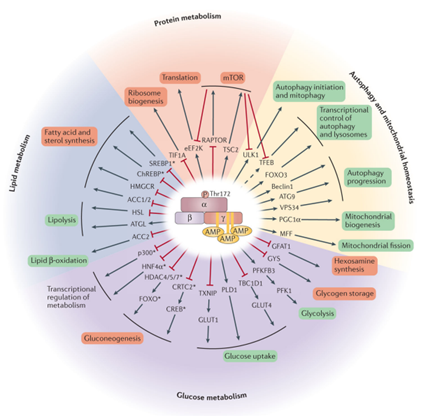
[Figure 1] The direct targets of AMPK are shown in the first concentric circle. The arrow indicates whether the phosphorylation is activating or inhibitory for the function of the target protein. The general process in which each target is involved is indicated in the next circle, and the box color indicates whether that general process is activated (green) or inhibited (red). The pathways modulated by AMPK are grouped into four general categories — protein metabolism, lipid metabolism, glucose metabolism, and autophagy and mitochondrial homeostasis — denoting the wide range of processes that are controlled by AMPK. (Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 19: 121).
Efficacy Of Actiponin®
Actiponin® containing Damulin A (Figure 2-1) and Damulin B (Figure 2-2) is a patented natural material from Gynostemma pentaphyllum. To measure efficacy of Actiponin® as an AMPK activator, L6 myotube cells were treated with Damulin A or Damulin B at different concentrations for 2 hours or AICAR (1 mM) as a positive control for 1 hour and were analyzed for levels of phosphorylation in AMPKα and acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC). Treatment of L6 myotube cells with Damulin A or Damulin B led to a dose-dependent increase in the phosphorylation of AMPKα at Thr172 (Figure 2A) and ACC at Ser79 (Figure 2B). These results confirm that Actiponin® functions as an AMPK activator via phosphorylation of AMPKα.
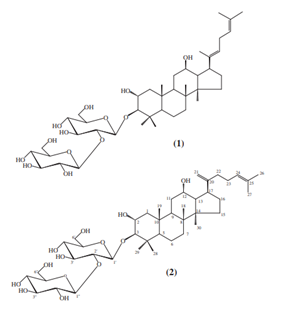
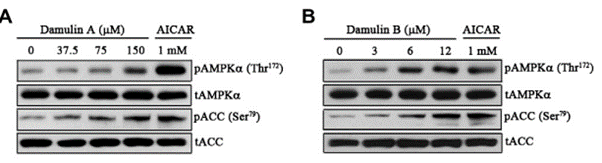
[Figure 2] Chemical structures of Damulin A (1) and B (2). Phosphorylation of AMPKα and ACC by Damulin A (panel A) and Damulin B (panel B); L6 myotube cells were exposed to different doses of Damulins A and B for 2 h or AICAR (1 mM) for 1 h, and phosphorylation of AMPKα was analyzed with western blot analysis. Damulins A and B increased phosphorylation of AMPKa and ACC in a dose-dependent manner.
The mice were orally administered with vehicle (saline) or Actiponin® (300 mg/kg/day) for 8 weeks. Cells isolated from the liver and skeletal muscles were analyzed for levels of AMPKα phosphorylation. Actiponin® containing Damulins A and B demonstrated 10 times better efficacy in phosphorylation of AMPKα, compared to other standardized extracts from G. pentaphyllum (Figure 3, Biotechnol Lett (2012) 34:1607).

[Figure 3] Oral treatment with Actiponin® increased AMPK and ACC phosphorylation in the soleus muscle and liver of mice. C57BL/6 male mice were treated with saline or Actiponin® (300 mg/kg) for 9 days, and AMPK and ACC phosphorylation in the soleus muscle (60 mg protein) and liver tissues (80 mg protein) were analyzed by western blot analysis.
AMPK on video
The video in two parts shows molecular and cellular mechanism how Actiponin® governs essential physiological processes in vivo and in vitro.

